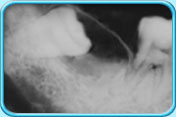
Usually seen in the lower jaw.
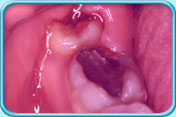
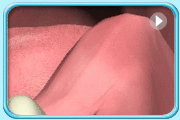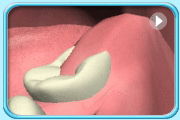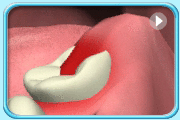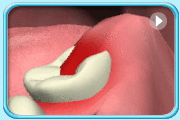
Food debris and bacteria are easily trapped in the space between the crown of the wisdom tooth and the overlying gingiva (gum), resulting in the infection of the surrounding tissues (Pericoronitis). Furthermore, the infected, swollen overlying gingiva is easily hurt by the opposing upper tooth making it difficult to recover.
Pericoronitis has the following signs and symptoms:
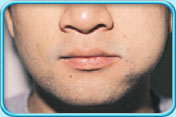
Pain and swelling of the cheek.
Since it is difficult to clean the surfaces between the impacted tooth and the adjacent tooth in front, dental plaque will accumulate there and cause tooth decay on these tooth surfaces.
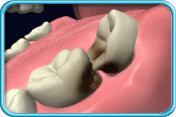
The inflammation of the surrounding tissues caused by the dental plaque, together with the pressure of the wisdom tooth pushing on the adjacent tooth in front, may cause the root of the adjacent tooth to resorb.

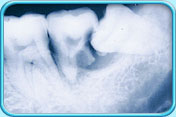
e.g. cysts.