

There are two factors causing tooth discoloration- internal factor and external factor.
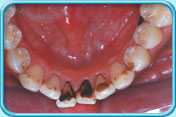 Teeth with black stains
Teeth with black stainsHabitual smoking or drinking of dark-coloured beverages, such as tea or coffee, result in the food colours being adsorbed onto the tooth surfaces.
The dentist will use:
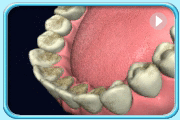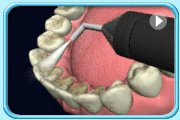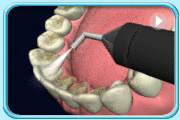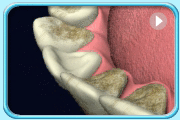 Prophyjet cleaning
Prophyjet cleaning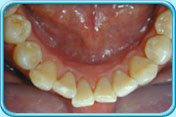 Teeth after black stain removal
Teeth after black stain removalDo not smoke and avoid drinking dark-coloured beverages to minimize food colours being adsorbed.
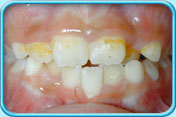 Teeth with orange stain
Teeth with orange stainTeeth has not been cleaned thoroughly, and the accumulated dental plaque contained bacteria or fungi that can produce colour and formed green and orange stains.
Dentist will perform scaling to remove accumulated dental plaque and stains.
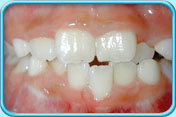 Teeth after orange stain removal
Teeth after orange stain removalBrush every morning and before bed at night, and use dental floss to remove dental plaque to keep the teeth white.
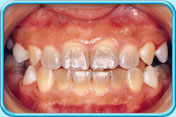
If there was certain sickness or, if tetracycline (a kind of antibiotics) is taken during the development of teeth, the teeth formed will be greyish-blue to brownish-yellow.
Tooth decay
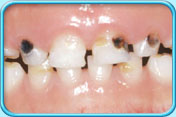
Treatment
The dentist removes the tooth decay, and then puts on a filling.
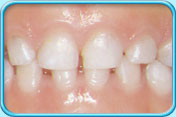
Pulp necrosis
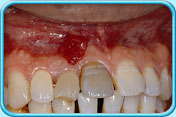
The pulp becomes necrotic because of tooth trauma or tooth decay, and the tooth will appear greyish-black.
Treatment
Endodontic treatment must be done to treat the discoloured tooth which has pulp necrosis.
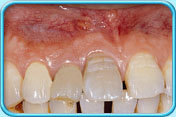 Tooth after root canal therapy
Tooth after root canal therapyIf teeth still appear greyish-black, dentist can treat the discolored teeth by bleaching , laminate veneer or crown.
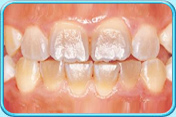
Disturbance during the development of tooth
If a deciduous tooth is so decayed that the pulp is exposed, the bacteria, via the apex of the tooth, will cause an infection in the vicinity of the developing permanent successor. This will disturb the development of the enamel of the permanent tooth, resulting in the formation of brownish-yellow patches.
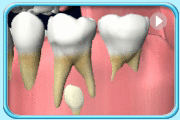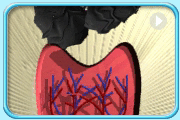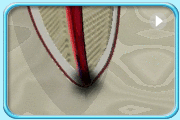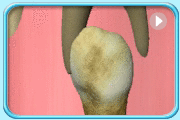
Early tooth decay
Dentist can apply topical fluoride onto the surfaces of teeth so that the early decay lesion can be remineralised.
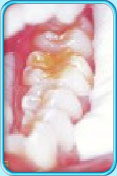
Disturbance during the development of a tooth or Fluorosis
Treatment such as Filling , Laminate veneer or Crown.
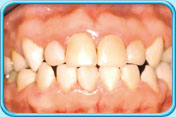 Tooth after filling
Tooth after filling