Amalgam has been used as a dental filling material for more than 150 years.
An alloy of mainly silver, tin, copper and mercury.
International dental health organization like the World Health Organization, Federation Dentaire International, and also the U.S. Food & Drug Administration have declared dental amalgam as safe and effective.
The followings are some queries about amalgam:
The greyish-silver colour of amalgam is not esthetically appealing.
It is mainly used for restoring back teeth where stress load is high.
Shape the filling, trim off excessive material, and polish the filling.
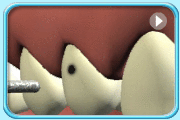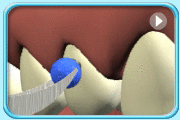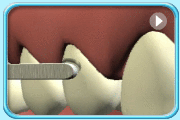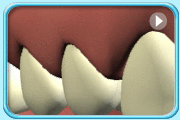
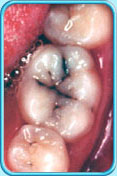 Before filling
Before filling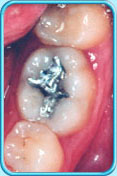 After filling
After filling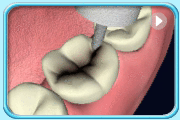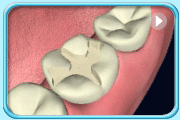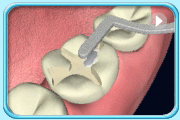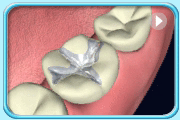
A substance made up of acrylic resin filled with inorganic substances such as glass, quartz as additives to enhance the strength.
Esthetic; colour is similar to that of natural teeth.
Not as hard as amalgam.
To restore decayed teeth.
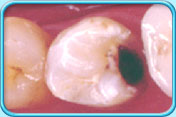 Before filling
Before filling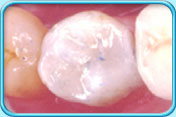 After filling
After fillingTo restore the appearance of the teeth, such as to modify the shape, size and colour of the teeth.
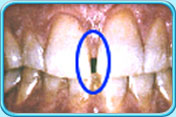 Before filling
Before filling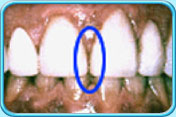 After filling
After fillingTrim off excessive material and polish the filling.
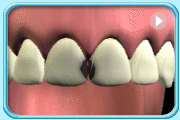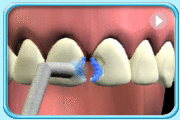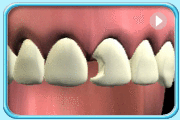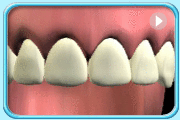
A substance made up of aluminosilicate glass powder and a liquid polyacrylic acid.
Insufficient strength to bear chewing force in long term, relatively low wear resistance.
Use on tooth surfaces that are not exposed to heavy chewing force, e.g. outer surface, to restore the abraded part.
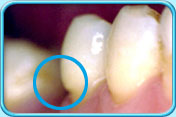 Before filling
Before filling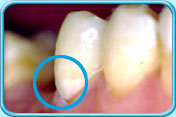 After filling
After fillingUse as filling material for deciduous teeth.
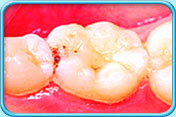 Before filling
Before filling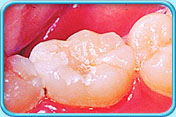 After filling
After fillingTrim off excessive material and polish the restoration.
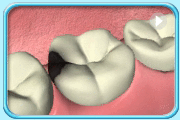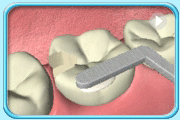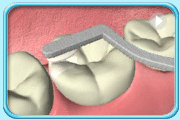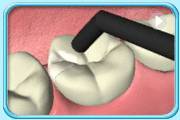
To increase the strength of Glass Ionomer Cement, acrylic resin is added. For this type of material, light curing is required to harden it.
It is a mixture of composite and glass ionomer cement.
Used as filling material for deciduous dentition.
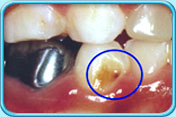 Before filling
Before filling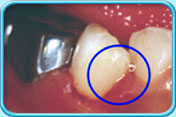 After filling
After fillingTrim the excessive material off and polish the restoration.